Blog 2
What is a Peer Reviewed Journal?

What is Peer Review?
Peer review is a process used in scholarly publishing to ensure the quality and validity of research papers before they are published in academic journals. It involves the evaluation of a manuscript by a panel of experts (peers) in the same subject area as the author(s) of the paper. Using strict criteria, the reviewers decide whether to accept each submission for publication.
Peer-reviewed articles are considered highly credible sources due to the rigorous process they go through before publication, hence contributing to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field.
What is a Peer Reviewed Journal?
A peer-reviewed journal, also known as a refereed or scholarly journal, is a type of academic publication that applies a process of peer review to evaluate and ensure the quality, validity, and credibility of submitted articles or research papers before they are published. The peer review process involves the thorough examination of the manuscript by independent experts in the same field as the authors.
Types of Peer Review
There are various types of peer review, and the choice of which type to use often depends on the preferences of the journal, conference, or academic institution:
- Single Blind Review
- In a single-blind review, the reviewers know the identity of the authors, but the authors are not aware of the identities of the reviewers.
- While single-blind review is intended to reduce bias by keeping authors unaware of the reviewers' identities, there is still a possibility of bias on the part of the reviewers.
- Double Blind Review
- In a double-blind review, both the reviewers and the authors are anonymous to each other.
- This type of review aims to eliminate potential biases that could arise from knowing the identities of the authors leading to manuscripts being published based more on merit than the author's reputation.
- Collaborative Review
- Collaborative peer review is when reviewers collaborate with others, either other reviewers or journal editors, or even the authors themselves, during the review process. However, the identity of the reviewer is not known to the author.
- This offers everyone involved a chance to address any contradictions or inconsistencies in real-time thus mitigating the need for multiple rounds of editing. However, this requires a set system in place to function effectively.
- Open Review
- In an open review, all parties know each other’s identities throughout the process.
- This type of review promotes transparency and accountability but can also lead to concerns about potential bias or reluctance to provide candid feedback.
Basics of Peer Review Process
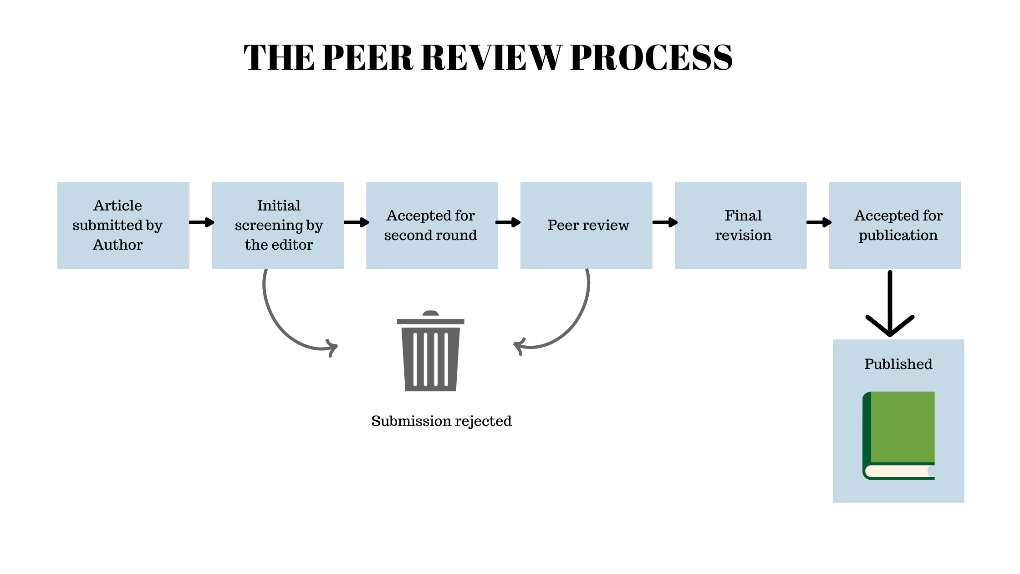
Here are the basic steps involved in the peer review process:
1. Authors submit their research manuscripts to the editor of a journal for consideration.
2. The editor first evaluates the submission and can either:
- Reject the manuscript and send it back to the author, or
- Send it onward to the selected peer reviewer(s)
3. The selected peer reviewers critically evaluate the manuscript. provide feedback, comments, and recommendations for revisions.
4. Authors receive the feedback from the reviewers and the editor. The edits are made and sent back to the editor for publication.
5. If accepted, the manuscript moves to the production stage for formatting, proofreading, and eventual publication in the journal.
Note: Although the above peer review process is a common framework, it's essential to recognize that each journal may have its specific procedures. Therefore, authors aspiring to publish in a particular journal should thoroughly go through their peer review guidelines.








